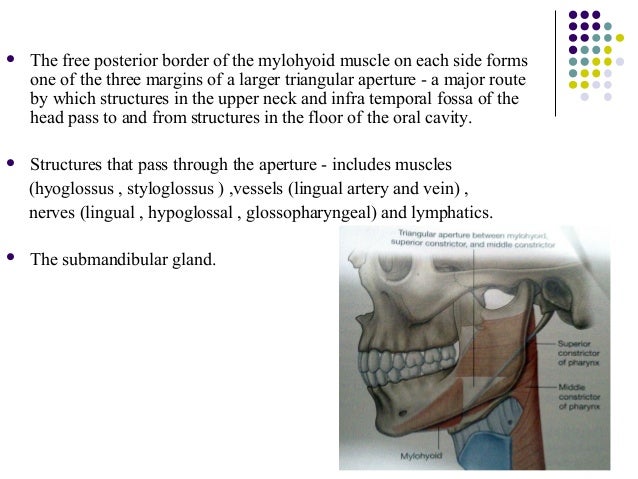
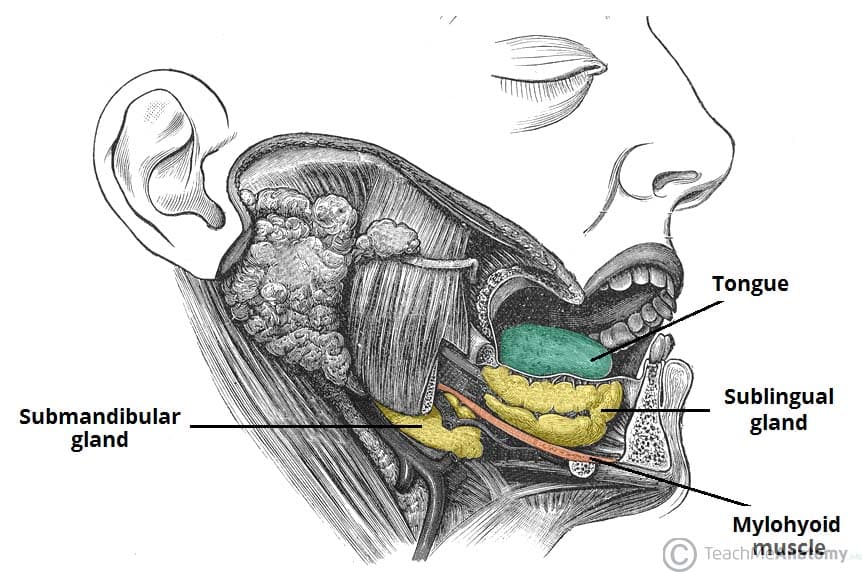
The squamous epithelium at the mucosal surface and other superficial anatomic components of the floor of the mouth are easily evaluated at physical examination the mylohyoid muscle sling is formed by the paired mylohyoid muscles which arise from the inner surface of the mandible extend from the symphysis anteriorly to the last molar tooth posteriorly and insert onto the posterior aspect.
Which muscle forms the floor of the mouth.
Which muscle of the floor of the mouth forms with the mandible a submandibular triangle on each side of the neck.
When cancer forms in this area it s called floor of mouth cancer.
However not all cysts affecting the floor of the mouth are cancerous.
In human anatomy the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva.
In rare circumstances oral cancer can affect this muscle.
Serous saliva is fluid.
One of the muscles that serves to form the floor or the mouth is the.
Dr nida sumra 2.
Floor of the mouth.
Which mandibular structure marks the insertion of the muscle that supports the floor of the mouth.
It is a pharyngeal muscle derived from the first pharyngeal arch and classified as one of the suprahyoid muscles.
The largest cranial nerve which innervates the maxilla and the mandible is the.
Forms a sling that supports the structures of the mouth origin.
The muscle of facial expression that compresses the cheeks against the teeth and retracts the angle of the mouth is the.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.
The parotid gland empties into the mouth through the stensen s duct.
The masseter muscles belong to which group of muscles of the head and neck.
Includes elevating the floor of the mouth and hyoid bone as well as depressing the mandible.
Watery and mainly protein.
Identify the secondary spinal curves.
The mylohyoid muscle is flat and triangular and is situated immediately superior to the anterior belly of the digastric muscle.
Together the paired mylohyoid muscles form a muscular floor for the oral cavity of the mouth.
Which muscle of the floor of the mouth forms with the mandible a submandibular triangle on each side of the neck.
Of the seven bones that form the orbital complex the and maxillary bones form the lateral wall and most of the orbital floor respectively.
The floor of the mouth is a small horseshoe shaped region situated beneath the movable part of the tongue and above the muscular diaphragm formed by the mylohyoid muscles and above this diaphragm is the genohyoid muscle.
The forms the support for the teeth of the maxillary arch.